学习一下Halo的缓存实现和使用场景
Halo的缓存实现的相关类位于
run/halo/app/cache下,主要应用场景:缓存token,验证码等业务数据和接口限流。
UML类图
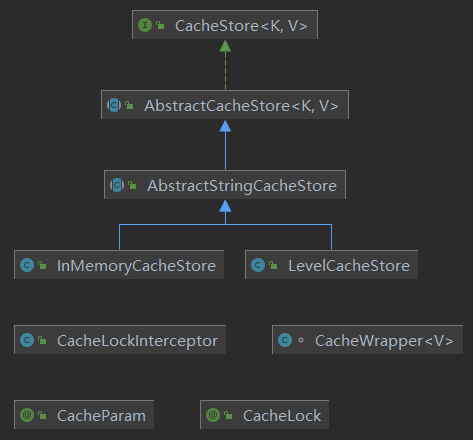
CacheStore
缓存的顶层接口类,定义使用行为
@NonNull
Optional<V> get(@NonNull K key);
void put(@NonNull K key, @NonNull V value, long timeout, @NonNull TimeUnit timeUnit);
void put(@NonNull K key, @NonNull V value);
/**
* 当缓存值过期了或者key不存在就放入值
*/
Boolean putIfAbsent(@NonNull K key, @NonNull V value, long timeout, @NonNull TimeUnit timeUnit);
void delete(@NonNull K key);
AbstractCacheStore
缓存的抽象实现类,定义通用方法,该类没有定义具体的缓存实现,只是定义了put时包装缓存值和get时清理过期值的行为。
@Slf4j
public abstract class AbstractCacheStore<K, V> implements CacheStore<K, V> {
//省略部分代码
/**
* 定义取值时清理过期值的行为
*/
@Override
public Optional<V> get(K key) {
Assert.notNull(key, "Cache key must not be blank");
return getInternal(key).map(cacheWrapper -> {
// Check expiration
if (cacheWrapper.getExpireAt() != null
&& cacheWrapper.getExpireAt().before(run.halo.app.utils.DateUtils.now())) {
// Expired then delete it
log.warn("Cache key: [{}] has been expired", key);
// Delete the key
delete(key);
// Return null
return null;
}
return cacheWrapper.getData();
});
}
//省略部分代码
@Override
public void put(K key, V value, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
putInternal(key, buildCacheWrapper(value, timeout, timeUnit));
}
@Override
public void put(K key, V value) {
putInternal(key, buildCacheWrapper(value, 0, null));
}
@Override
public Boolean putIfAbsent(K key, V value, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
return putInternalIfAbsent(key, buildCacheWrapper(value, timeout, timeUnit));
}
/**
* 包装缓存值
*/
@NonNull
private CacheWrapper<V> buildCacheWrapper(@NonNull V value, long timeout,
@Nullable TimeUnit timeUnit) {
Assert.notNull(value, "Cache value must not be null");
Assert.isTrue(timeout >= 0, "Cache expiration timeout must not be less than 1");
Date now = run.halo.app.utils.DateUtils.now();
Date expireAt = null;
if (timeout > 0 && timeUnit != null) {
expireAt = DateUtils.add(now, timeout, timeUnit);
}
// Build cache wrapper
CacheWrapper<V> cacheWrapper = new CacheWrapper<>();
cacheWrapper.setCreateAt(now);
cacheWrapper.setExpireAt(expireAt);
cacheWrapper.setData(value);
return cacheWrapper;
}
}
AbstractStringCacheStore
缓存的抽象实现类,定义通用方法,该类不定义缓存具体实现,而是定义缓存的存取值过程中的序列、反序列化的实现,这里用的Jackson的ObjectMapper
@Slf4j
public abstract class AbstractStringCacheStore extends AbstractCacheStore<String, String> {
protected Optional<CacheWrapper<String>> jsonToCacheWrapper(String json) {
Assert.hasText(json, "json value must not be null");
CacheWrapper<String> cacheWrapper = null;
try {
cacheWrapper = JsonUtils.jsonToObject(json, CacheWrapper.class);
} catch (IOException e) {
log.debug("Failed to convert json to wrapper value bytes: [{}]", json, e);
}
return Optional.ofNullable(cacheWrapper);
}
public <T> void putAny(String key, T value) {
try {
put(key, JsonUtils.objectToJson(value));
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
throw new ServiceException("Failed to convert " + value + " to json", e);
}
}
public <T> void putAny(@NonNull String key, @NonNull T value, long timeout,
@NonNull TimeUnit timeUnit) {
try {
put(key, JsonUtils.objectToJson(value), timeout, timeUnit);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
throw new ServiceException("Failed to convert " + value + " to json", e);
}
}
public <T> Optional<T> getAny(String key, Class<T> type) {
Assert.notNull(type, "Type must not be null");
return get(key).map(value -> {
try {
return JsonUtils.jsonToObject(value, type);
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Failed to convert json to type: " + type.getName(), e);
return null;
}
});
}
}
CacheWrapper
缓存值包装对象
/**
* Cache data
*/
private V data;
/**
* Expired time.
*/
private Date expireAt;
/**
* Create time.
*/
private Date createAt;
InMemoryCacheStore
缓存的内存缓存实现,实现用的是ConcurrentHashMap,并发安全
@Slf4j
public class InMemoryCacheStore extends AbstractStringCacheStore {
/**
* Cleaner schedule period. (ms)
*/
private static final long PERIOD = 60 * 1000;
/**
* Cache container.
*/
private static final ConcurrentHashMap<String, CacheWrapper<String>> CACHE_CONTAINER =
new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Timer timer;
/**
* Lock.
*/
private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
//创建定时器,每分钟遍历一次ConcurrentHashMap,清理过期值
public InMemoryCacheStore() {
// Run a cache store cleaner
timer = new Timer();
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new CacheExpiryCleaner(), 0, PERIOD);
}
@Override
@NonNull
Optional<CacheWrapper<String>> getInternal(@NonNull String key) {
Assert.hasText(key, "Cache key must not be blank");
return Optional.ofNullable(CACHE_CONTAINER.get(key));
}
@Override
void putInternal(@NonNull String key, @NonNull CacheWrapper<String> cacheWrapper) {
Assert.hasText(key, "Cache key must not be blank");
Assert.notNull(cacheWrapper, "Cache wrapper must not be null");
// Put the cache wrapper
CacheWrapper<String> putCacheWrapper = CACHE_CONTAINER.put(key, cacheWrapper);
log.debug("Put [{}] cache result: [{}], original cache wrapper: [{}]", key, putCacheWrapper,
cacheWrapper);
}
@Override
Boolean putInternalIfAbsent(@NonNull String key, @NonNull CacheWrapper<String> cacheWrapper) {
Assert.hasText(key, "Cache key must not be blank");
Assert.notNull(cacheWrapper, "Cache wrapper must not be null");
log.debug("Preparing to put key: [{}], value: [{}]", key, cacheWrapper);
lock.lock();
try {
// Get the value before
Optional<String> valueOptional = get(key);
if (valueOptional.isPresent()) {
log.warn("Failed to put the cache, because the key: [{}] has been present already",
key);
return false;
}
// Put the cache wrapper
putInternal(key, cacheWrapper);
log.debug("Put successfully");
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public void delete(@NonNull String key) {
Assert.hasText(key, "Cache key must not be blank");
CACHE_CONTAINER.remove(key);
log.debug("Removed key: [{}]", key);
}
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy() {
log.debug("Cancelling all timer tasks");
timer.cancel();
clear();
}
private void clear() {
CACHE_CONTAINER.clear();
}
/**
* 清理缓存用的定时器
*/
private class CacheExpiryCleaner extends TimerTask {
@Override
public void run() {
CACHE_CONTAINER.keySet().forEach(key -> {
if (!InMemoryCacheStore.this.get(key).isPresent()) {
log.debug("Deleted the cache: [{}] for expiration", key);
}
});
}
}
}
InMemoryCacheStore是Halo的默认缓存提供类,可以看到在父抽象类的基础上,多了:定时器去定时清理过期值、putInternalIfAbsent的具体实现。
putInternalIfAbsent方法是Halo实现接口限流的重要方法,通过key判断值是否存在或过期,来达到指定时间内只能访问一次的功能。putInternalIfAbsent方法使用了ReentrantLock锁,这是因为虽然ConcurrentHashMap本身是线程安全的,但是这里做限流功能的方法实现里,有个取值然后比较的操作,这个操作不是原子的。当多个线程进入方法取值进行判断时,可能出现if (valueOptional.isPresent())都为false的判断,然后都会put值然后返回true,这样就结果就不正确了,就无法起到限流的作用。
LevelCacheStore
缓存的内嵌式数据库实现,除了实现是Google的LevelDB数据库外,其他方法跟InMemoryCacheStore区别不大,不再描述
CacheLock、CacheLockInterceptor、CacheParam
缓存的使用:接口限流
CacheLock注解作为切点,CacheLockInterceptor为切面类,CacheParam为使用限流时的额外参数,具体的使用看Halo登陆模块详解
自定义Redis缓存实现
看了Halo的缓存模块后,虽然实现挺简单的,但是类设计上值得学习,思路清晰。不像自己有时候写着写着类的功能要么冗余了要么职责不清了。
最近在学习Redis的使用,就打算在Halo上再加一个Redis的缓存实现。用来练习一下。
新建一个RedisCacheStore类。我打算还是用Jackson的方法进行序列、反序列化,就继承与AbstractStringCacheStore吧。需要实现以下抽象方法:
@Override
Optional<CacheWrapper<String>> getInternal(String key) {
return Optional.empty();
}
@Override
void putInternal(String key, CacheWrapper<String> cacheWrapper) {
}
@Override
Boolean putInternalIfAbsent(String key, CacheWrapper<String> cacheWrapper) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void delete(String key) {
}
操作Redis我打算用Spring提供的RedisTemplate,由于RedisTemplate需要自己提供序列化转化器,不提供的话默认使用的是JdkSerializationRedisSerializer,它只支持实现了序列化接口的对象,如果放入String的话,存入的是String的序列化对象,可读性跟String的byte数组比差太多。于是使用RedisTemplate的子类StringRedisTemplate
在Halo的java config类run/halo/app/config/HaloConfiguration.java里加一个bean定义:
@Bean
public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate() {
JedisPoolConfig poolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig();
// 最大空闲数
poolConfig.setMaxIdle(50);
// 最大连接数
poolConfig.setMaxTotal(100);
// 最大等待毫秒数
poolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(20000);
StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate = new StringRedisTemplate();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(new JedisConnectionFactory(poolConfig));
return redisTemplate;
}
build.gradle加入依赖
implementation 'org.springframework.data:spring-data-redis:2.5.0'
implementation 'redis.clients:jedis:3.6.0'
加上实现细节
public class RedisCacheStore extends AbstractStringCacheStore {
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
public RedisCacheStore(StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate) {
this.stringRedisTemplate = stringRedisTemplate;
}
@Override
Optional<CacheWrapper<String>> getInternal(String key) {
Assert.hasText(key, "Cache key must not be blank");
String valueJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
return StringUtils.isEmpty(valueJson) ? Optional.empty() :
jsonToCacheWrapper(valueJson);
}
@Override
public Optional<String> get(String key) {
return getInternal(key).map(cacheWrapper -> cacheWrapper.getData());
}
@Override
void putInternal(String key, CacheWrapper<String> cacheWrapper) {
try {
if (cacheWrapper.getExpireAt() != null) {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JsonUtils.objectToJson(cacheWrapper),
getDuration(cacheWrapper.getCreateAt(), cacheWrapper.getExpireAt()));
} else {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JsonUtils.objectToJson(cacheWrapper));
}
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
throw new ServiceException("Failed to convert " + cacheWrapper + " to json",
e);
}
}
Duration getDuration(Date start, Date end) {
LocalDateTime s = LocalDateTime.ofInstant(start.toInstant(), ZoneId.systemDefault());
LocalDateTime e = LocalDateTime.ofInstant(end.toInstant(), ZoneId.systemDefault());
return Duration.between(s, e);
}
@Override
Boolean putInternalIfAbsent(String key, CacheWrapper<String> cacheWrapper) {
try {
if (cacheWrapper.getExpireAt() != null) {
return stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue()
.setIfAbsent(key, JsonUtils.objectToJson(cacheWrapper),
getDuration(cacheWrapper.getCreateAt(), cacheWrapper.getExpireAt()));
} else {
return stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue()
.setIfAbsent(key, JsonUtils.objectToJson(cacheWrapper));
}
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
throw new ServiceException("Failed to convert " + cacheWrapper + " to json",
e);
}
}
@Override
public void delete(String key) {
stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);
}
}
能看到Redis的缓存实现没有定时器,因为清理过期值的工作交给了redis,不用自己写个定时器定时遍历和get取值时去判断过期值。
最后修改配置:
switch (haloProperties.getCache()) {
case "level":
stringCacheStore = new LevelCacheStore(this.haloProperties);
break;
case "redis":
stringCacheStore = new RedisCacheStore(stringRedisTemplate);
break;
case "memory":
default:
//memory or default
stringCacheStore = new InMemoryCacheStore();
break;
}
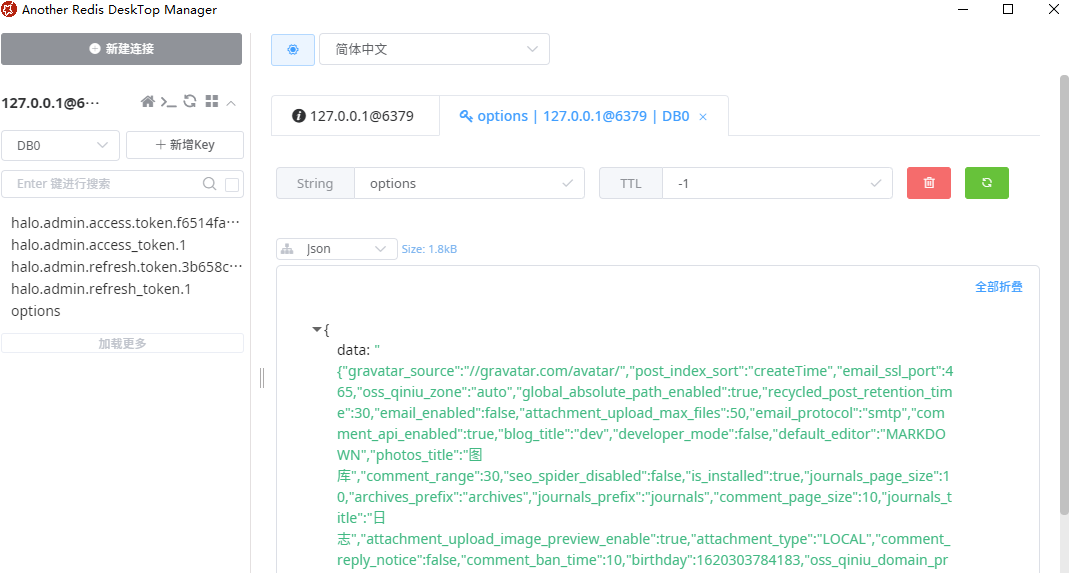
启动后登录看下结果:
总结
- 功能模块在设计时要有良好的抽象,便于后续功能扩展和具体实现的变更。
- 缓存除了缓存业务数据,内存缓存还能做限流访问的标识,因为内存速度快。
- Halo的内存缓存实现符合Halo的使用场景,没有什么高并发,只缓存很少的业务数据,所以以下缺点可忽略:
- 因为是开一个线程去遍历清理过期对象,缓存多了后会时间变长
- 缓存越来越多了后,内存吃紧时没有能让GC释放掉的机会,会OOM
如果要实现一个避开以上缺点的缓存,可以用DelayQueue和SoftReference
Q.E.D.



